
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
16.11.2023
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) , Daily Current Affairs , RACE IAS : Best IAS Coaching in Lucknow
|
For Prelims:About Helicobacter Pylori,Important points,Helicobacter pylori infection,symptoms, Background of H. pylori |
Why in the news?
Recently the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases has made possible the rapid detection of drug-resistant 'Helicobacter pylori'.
Important points:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) A two-step PCR-based assay of a small area of bacteria can help detect H. pylori infection.
- It can also identify clarithromycin-resistant bacteria and drug-sensitive bacteria in six-seven hours.
- It has been developed by a team of researchers from the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Disease (ICMR-NICED), Kolkata.
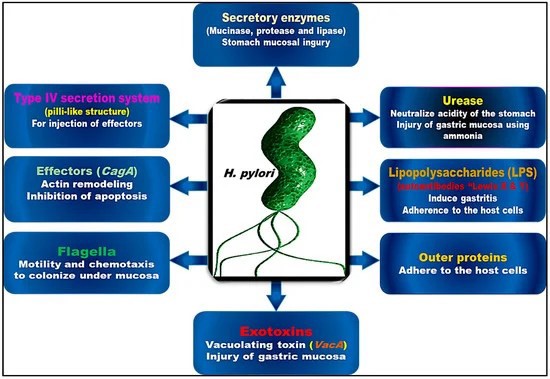
About Helicobacter Pylori:
- This is a common type of bacteria that grows in the digestive tract and attacks the lining of the stomach.
- H. pylori is commonly associated with chronic active gastroenteritis, and the bacteria reside in glands beneath the mucosal surface.
- Its infections are usually harmless, but it has been linked to gastrointestinal issues such as peptic ulcers and stomach cancer.
- Several extragastric complications, such as iron deficiency anemia, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, vitamin B12 deficiency, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, and certain neurological disorders, have also been associated with H. pylori infection.
- It is present in the body of about two-thirds of the world's population.
- In India, H. pylori infection affects 60–70% of the population.
- This usually occurs during childhood.
- The spiral shape of H. pylori allows it to penetrate the lining of the stomach, where it is protected by mucus and cannot be reached by the body's immune cells.
Helicobacter pylori infection:
- There is no clear information about how this bacteria is spread, but person-to-person transfer through oral or fecal contact is thought to be the predominant method.
symptoms:
- Most people with H. pylori infection never have any signs or symptoms.
- When signs or symptoms of H. pylori infection appear, they are usually related to gastritis or peptic ulcers and may include:
- Stomach pain or burning.
- Stomach pain (extreme when your stomach is empty).
- nausea.
- loss of appetite.
- Frequent belching.
- Swelling.
- Unintentional weight loss.
Treatment:
- Clarithromycin is an antibiotic commonly used to treat H. pylori infections, but drug-resistant strains in India have raised concerns about its effectiveness.
- Clarithromycin usually involves a combination of antibiotics and a proton-pump inhibitor (a medicine that reduces the acid in your stomach) for up to 14 days.
- If not treated effectively with antibiotics, it remains in the stomach for life.
- This treatment is sometimes called triple therapy.
Background of H. pylori:
- It is estimated that H. pylori was found in an infected person in Africa about 60,000 years ago.
- H. pylori was found in contemporary animals before people migrated out of Africa and eventually in humans.
- In early 1982, Doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren of Perth, Western Australia, discovered H. pylori in patients suffering from inflammation and ulcers in the gastric mucosa.
- A widespread belief at the time was that microbes could not survive in the acidic environment of the stomach.
- As a result of Marshall and Warren's discovery, they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005. Marshall and Warren's study was the first to find spiral-shaped bacteria in the stomach wall.
However, German researchers were not able to develop them, so their findings were ignored.