
Solid-fuel Missiles
21-12-2023
Solid-fuel Missiles
|
For Prelims: WHAT IS SOLID-FUEL TECHNOLOGY?, Key Points, SOLID VS LIQUID, intercontinental ballistic missile, Ballistic Missile |
Why in the news?
Recently, North Korea test-fired an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) powered by solid fuel .
Key Points
- The Soviet Union fielded its first solid-fuel ICBM, the RT-2, in the early 1970s.
- China started testing solid-fuel ICBMs in the late 1990s.
- Solid-fuel missiles do not need to be fuelled immediately ahead of launch.
- They are often easier and safer to operate, and require less logistical support.
- They are harder to detect and more survivable than liquid-fuel weapons.
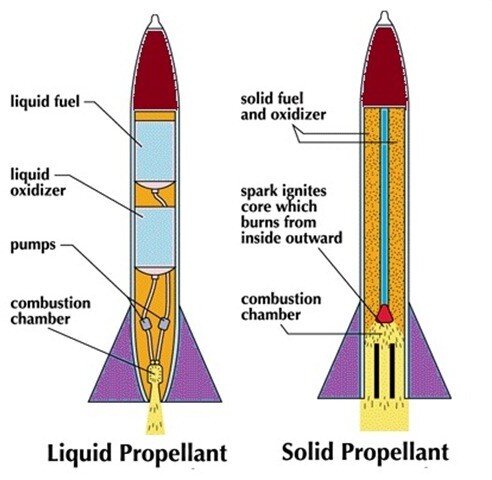
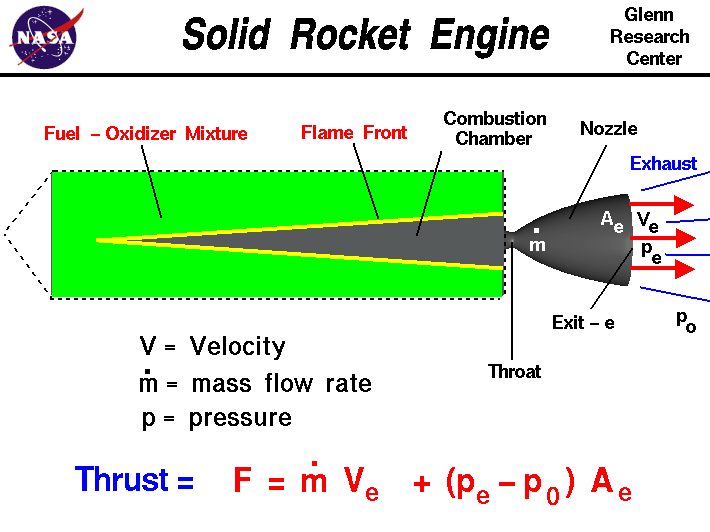
WHAT IS SOLID-FUEL TECHNOLOGY?
- Solid propellants are a mixture of fuel and oxidiser.
- Metallic powders such as aluminium often serve as the fuel, and ammonium perchlorate, which is the salt of perchloric acid and ammonia, is the most common oxidiser.
- The fuel and oxidiser are bound together by a hard rubbery material and packed into a metal casing.
- When solid propellant burns, oxygen from the ammonium perchlorate combines with aluminium to generate enormous amounts of energy and temperatures of more than 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit (2,760 degrees Celsius), creating thrust and lifting the missile from the launch pad.
SOLID VS LIQUID
- Liquid propellants provide greater propulsive thrust and power, but require more complex technology and extra weight.
- Solid fuel is dense and burns quite quickly, generating thrust over a short time. Solid fuel can remain in storage for an extended period without degrading or breaking down - a common issue with liquid fuel.
Notable Examples of Solid-Fuel Missiles:
USA: Minuteman III, Trident II (D5).
Russia: Topol-M, Yars, Bulava.
China: DF-31, DF-41.
North Korea: Pukkuksong Series (KN-11, KN-15).
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM)
- It is a missile with a minimum range of 5,500 kilometres primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery.
- Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs.
- Countries that have ICBMs: India, Russia, the United States, North Korea, China, Israel, the United Kingdom and France.
- ICBMs are differentiated by having greater range and speed than other ballistic missiles.
- Short and medium-range ballistic missiles are known collectively as the theater ballistic missiles.
Ballistic Missile
- It is a rocket-propelled self-guided strategic-weapons system that follows a ballistic trajectory to deliver a payload from its launch site to a predetermined target.
- Ballistic missiles are powered initially by a rocket or series of rockets in stages, but then follow an unpowered trajectory that arches upwards before descending to reach its intended target.
- Ballistic missiles can carry either nuclear or conventional warheads.
Source: Reuters. Com