India's Growing Aspirations in Arctic
India's Growing Aspirations in Arctic
GS-1,2,3: Geographical phenomena, Govt. policies, Environmental protection
(IAS/UPPCS)
Relevant for Prelims:
About the Arctic Region, Svalbard Treaty-1920, Himadri, National Center for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Svalbard Archipelago, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Relevant for Mains:
India's Arctic policy, India's aspirations, Significance of the Arctic region, Emerging challenges, Way forward, Conclusion.
20/04/2024
Source: TH
Context:
In March 2024, India's first winter expedition to the Arctic region ended successfully. This expedition was related to Himadri for which in December 2023, four Indian climate scientists left for Norway in the Arctic.
- This expedition allowed Indian Scientific Expeditionary Researchers to make unique scientific observations during the polar nights in the Arctic during winter (November to March), where there is no sunlight for almost 24 hours and the temperature is below zero (less than -15 degrees Celsius).
- This will help increase understanding of the Arctic, especially climate change, space weather, sea-ice and ocean circulation dynamics, ecosystem adaptation, etc., which affect weather and climate in the tropical regions, including monsoon.
India's Arctic Policy:
- India's Arctic Policy includes Science and Research; Environment protection; Economic and Human development; Transportation and Connectivity; Governance and International Cooperation; and National capacity building.
- Its objective is to strengthen national capabilities and competencies in science and exploration, climate and environmental protection, maritime and economic cooperation with the Arctic region.
- India's Arctic policy will be implemented through an action plan and an effective governance and review mechanism involving an inter-ministerial empowered Arctic Policy Group.
- The implementation of India's Arctic policy will involve multiple stakeholders including academia, research community, business and industry.
India's aspirations in the Arctic region:
- India is looking for immense potential in the Arctic region. For this, India is likely to get cooperation with Denmark and Finland in areas like waste management, pollution control, renewable energy and green technology.
- Many believe that the partnership with Norway could be transformative for India as it would enable greater Indian participation in Arctic Council working groups. This will address issues like blue economy, connectivity, maritime transport, investment and infrastructure and responsible resource development.
- The Indian government is keen to benefit from marine mining and resource exploitation in the Arctic region, so it should clearly support a sustainable method of extraction.
- India is excited by the opening of Arctic sea routes, primarily the Northern Sea Route, and would like to expand Indian trade through this region.
- This can help reduce time, fuel and security costs as well as costs for shipping companies in sending goods to India.
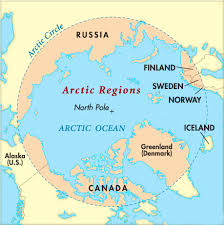
About Arctic Region:
Geographical location:
- This region is the area above the latitude 66° 34′ north of the Arctic Circle.
- This region includes eight countries – Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and America. All these countries are members of the Arctic Council.
- This region experiences extremely cold temperatures, especially during winter, with most of the region covered with snow.
Climate and Environment:
- The Arctic is characterized by its cold climate, where temperatures often drop below zero.
- The region is covered with ice, including sea ice and ice caps, which play an important role in regulating Earth's climate by reflecting sunlight.
- The Arctic is home to a unique ecosystem, home to polar bears, seals, whales and various species of birds.
Significance of the Arctic region:
Economic significance:
- The Arctic region is a storehouse of 22% unknown resources. This region has rich and ample reserves of coal, gypsum, diamonds, zinc, lead, placer gold and quartz.
- Currently 25% reserves of rare earth elements exist in Greenland.
- The Arctic also has large reserves of unexplored hydrocarbon resources, which account for 30% of the world's undiscovered natural gas.
- Thus, the Arctic can potentially address India's energy security needs and shortage of strategic and rare earth minerals.
Geographical significance:
- The Arctic helps the world's ocean currents circulate and move cold and warm water around the globe.
- Additionally, Arctic sea ice acts as a giant white reflector on the planet's surface, bouncing some of the sun's rays back into space, helping to keep the Earth at a uniform temperature.
Geopolitical significance:
- The melting of Arctic ice is also raising geopolitical temperatures to levels not seen since the Cold War. China has referred to the trans-Arctic shipping routes as the 'Polar Silk Road' marking it as the third transport corridor for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and apart from Russia, it is the only country which is building a 'nuclear ice-breaker'.
- In this scenario, it is extremely important to counter China's soft power moves in the Arctic and in this sequence, India is also taking keen interest in the Arctic states through its Arctic policy.
Environmental significance:
- The Arctic and the Himalayas, although geographically distant, are interconnected and share common concerns. The melting of the Arctic is helping the scientific community to better understand the melting of glaciers in the Himalayas. It is noteworthy that the Himalayas are often called the 'third pole' and it holds the largest reserves of fresh water after the North and South Poles.
India's presence in Arctic:
- India's involvement in the region dates back to 1920 with the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in Paris.
- In 2007, India launched its first research mission to investigate Arctic microbiology, atmospheric science and geology.
- In 2008, India became the only developing country other than China to establish an Arctic research base called Himadri.
- It hosts scientists mostly during summer (April to October).
- After being granted 'observer' status by the Arctic Council in 2013, India launched a multi-sensor moored observatory in Svalbard in 2014 and an atmospheric laboratory in 2016.
- In December 2023, the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences launched India's first winter scientific expedition to the Arctic region.
- The expedition is related to the country's Arctic research station “Himadri” located in Ny-Ålesund within the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard.
- The first batch of the expedition includes researchers from the host National Center for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Mandi, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and Raman Research Institute.
- Work at these stations focuses on investigating the consequences of Arctic melting on Arctic ice systems and glaciers and the Himalayas and the Indian monsoon.
Emerging Challenges:
- The issue of Indian involvement in the Arctic divides the country's academic and policy communities.
- Opinion is divided on the potential impacts of changing climate in the Arctic on India's economy.
- Concerns arise primarily from mining in the region for fossil fuels, an area where India has not yet formulated a clear economic strategy.
- Proponents of economic exploitation in the Arctic advocate a pragmatic approach to the region, particularly oil and gas exploration and mining.
- Skeptics warn about potential environmental consequences and stress the need for a more balanced policy framework that recognizes the negative aspects of marine resource exploitation.
- China's increasing investment in the Arctic has increased India's concern.
- Russia's decision to grant China expanded access to the Northern Sea Route has deepened this concern.
- India's focus on the Arctic comes at a time when tensions in the region have increased, fueled by the Russia-Ukraine conflict and the suspension of various regional cooperative forums.
Way forward:
- The Arctic is a very important region in many ways; Therefore, scientists have to play a vital role in addressing the areas that affect life and existence on this planet.
- India needs to seek cooperation from Norway to effectively implement its Arctic policy as it can meet the needs of Indian scientists in terms of research in this region.
- Partnership with Norway is likely to focus on scientific research and climate and environmental protection.
- Since global geopolitical tensions are also rising in the Arctic, it would be in the interest of both India and Norway to find constructive and non-sensitive ways to reduce pressure.
- India's Arctic Policy will play an important role in preparing the country for a future where mankind's greatest challenges like climate change can be addressed through collective will and effort.
Conclusion:
The Arctic region is a highly sensitive ecosystem that can play a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate, meeting India's aspirations. However, it is facing unprecedented environmental changes due to climate change, including rapid ice melting and rising temperatures.
There is a special need for international cooperation to preserve the Arctic's sensitive environment and ensure its long-term viability.
-------------------------------------------
Mains Question
Why are India's aspirations so high from the Arctic region? Discuss the emerging challenges in the Arctic region and solutions to overcome them.