Global Slavery Index, 2023
Global Slavery Index, 2023
Mains Exam: General Studies Paper 2
(Government Policy Issues)
In News:
- Recently, the Global Slavery Index, 2023 report has been released.
Key findings of this report:
- This report has presented an assessment of people living in "modern slavery" in 160 countries.
- According to this report, on any given day in the year 2021, 50 million or more than 50 million people were living in "modern slavery".
- Of the 50 million people living in modern slavery, 28 million are victims of forced labor and 22 million are victims of forced marriage.
- Of these 50 million modern slaves, 12 million are children.
What is the meaning of Modern slavery?
- Modern slavery refers to situations in which a person cannot refuse or leave because of threat, violence, coercion, deception or abuse of power.
- Modern slavery includes a variety of practices such as forced labor, forced marriage, debt bondage, sexual exploitation, human trafficking, slavery-like practices, forced or servile marriage, the sale of children, and exploitation.
Global Slavery Index:
- This is the fifth edition of the Global Slavery Index.
- This index is issued by "Walk Free" human rights organization.
- The data on modern slavery in this report has been obtained from the International Labor Organization (ILO), Walk Free and the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
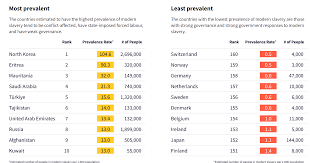
Ten countries with the highest prevalence of slavery:
- North Korea, Eritrea, Mauritania, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Tajikistan, United Arab Emirates, Russia, Afghanistan and Kuwait.
Ten countries with the least prevalence of slavery:
- Switzerland, Norway, Germany, Netherlands, Sweden, Denmark, Belgium, Ireland, Japan and Finland.
The ten countries with the largest number of people living in modern slavery:
- India, China, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey, Bangladesh, United States of America.
- Asia and the Pacific account for the largest number of people in modern slavery, currently at 29.3 million.
The countries with the largest number of people living in modern slavery are the 6 members of the G20 countries:
- India, China, Russia, Indonesia, Türkiye and USA.
Steps taken against slavery in the world:
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations: Goal 8.7 of the SDGs calls for ending modern slavery, trafficking and child labour.
- In the year 2018, Australia passed the 'Modern Slavery Act', in which companies that have a consolidated revenue of more than AU$100 million per year,they are mandated to report on the action they are taking to stop modern slavery.
- About 137 countries have criminalized human trafficking in accordance with the UN Trafficking Protocol.
Steps taken against slavery in India:
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 23 of the Constitution: Prohibits human trafficking and any form of begar and forced labour.
- Article 24 of the Constitution: Prohibits the employment of any child below the age of fourteen years in any factory or mine or in any other hazardous employment.
- India has ratified the two fundamental ILO conventions relating to the elimination of child labour, the Minimum Age Convention, 1973 (No. 138) and the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labor Convention, 1999 (No. 182).
- Bonded Labor Abolition Act of 1976: This Act prohibits bonded labor and forced labour, and identifies the responsibilities of state governments to constitute Vigilance Committees. The act was amended in 1985 to include contract and migrant workers.
- Central Scheme for Rehabilitation of Bonded Labour: This scheme provides financial assistance to the rescued persons.
Concerns:
- Lack of clear definition: There is no clear international legal definition of 'modern slavery', which sometimes leads to difficulties in providing assistance at the international or national level.
- Ranking Methodology: The data in the index ignores qualitative analysis.
- Ranking countries in this way is humiliating for poorer countries.
Way Forward:
- The sources of goods and services related to modern slavery can be blocked by governments and organizations through appropriate action and legislation.
- Anti-slavery measures should be included in climate change sustainability plans.
- Compulsory primary and secondary education should be provided to the children.
- Laws of forced and child marriage should be strictly implemented.
- G20 countries must ensure strong legislation and accountability to empower vulnerable communities.
- There is a need to ensure people's access to public goods and decent work to prevent forced labour.
Source: Indian Express, The Hindu
-----------------------------------