“Digital Public Infrastructure(DPI)” Report
“Digital Public Infrastructure(DPI)” Report
GS-2: e-Governance
(UPSC/State PSC)
Important for Prelims:
DPI Report, Digital Public Framework, NASSCOM, India Stack, Application Programming Interface, Digital India.
Important for Mains:
About Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), DPI report, Recommendations, Significance/achievements, Challenges in adopting DPI, Way forward, Conclusion.
27/02/2024
Why in news:
Recently, software companies' body NASSCOM and management consultancy firm Arthur D Little have released a report titled “DPI of India – Accelerating India's Digital Inclusion” on revenues from digital public infrastructure (DPI).
Main points:
- Revenue from DPI has contributed 0.9% (total $31.8 billion) to the country's GDP in the year 2022.
- According to NASSCOM estimates, the contribution of DPI to GDP will be 2.9 -4.2% by the year 2030.
- DPI will lead India towards a $1 trillion digital economy by 2030.
- According to the report, more than 30 countries are currently either adopting or planning to implement India's DPI like UPI and Aadhaar in their countries to promote social and financial inclusion.
Recommendations to enhance the capacity of DPI:
- Innovative technologies should be used to integrate digital systems.
- Awareness should be increased about the use of existing digital systems.
- Innovation should be promoted through partnerships with the private sector.
- Products and services should be created to take advantage of existing DPIs; Etc.
About Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI):
- It is a collection of digital platforms and technologies; Like Aadhaar, Digital Locker, DigiYatra, UPI etc.
- These technologies are developed through collaboration between various entities including governments, regulators, private sector, volunteers.
Objective of Digital Public Infrastructure:
- Widely promoting digitalization services
- To ensure access of social services to the people of the country
- Providing economic opportunities to people in a safe manner
Significance/Achievements:
e-Governance and Transparency:
- Better service delivery: DPIs streamline government services, reduce manual processes and corruption, leading to greater efficiency and transparency.
- Citizen-centric: DPIs empower citizens with better access to government services, information and opportunities, by promoting participation and accountability.
- Reduction in corruption: Transparency through online services and digital transactions reduces the scope for corruption, thereby promoting better governance practices.
Economic Impact:
- Financial Inclusion: DPIs like Aadhaar and UPI connected millions of people to the formal financial system, facilitating easy access to credit and financial services.
- Boosting the digital economy: DPIs support digital transactions, e-commerce and online businesses, accelerating economic growth and creating new opportunities.
Social Impact:
- Improved public health: DPIs can aid in health care delivery, disease surveillance, and telemedicine, thereby increasing access to quality health care in remote areas.
- Government initiatives like Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission and National Health Mission leverage DPI in health care.
- Education and skill development: DPIs facilitate online learning platforms, digital content access and skill development programmes, promote knowledge dissemination and improve employability.
- Sustainable Development Goals: DPIs can play an important role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in India.
- National Security: Strong DPIs can assist in e-surveillance and intelligence gathering, helping to maintain national security.
- Disaster management: DPIs can facilitate early warning systems, resource allocation, and communications during natural disasters, thereby improving response effectiveness.
- International Collaboration: India's DPIs are gaining global recognition, attracting investments and promoting international partnerships in technological development.
- Currently, Bhutan, France, UAE, Singapore and Sri Lanka have included UPI in their digital systems.
Challenges in adopting DPI:
- Digital divide: Unequal access to the Internet and digital literacy hinders widespread adoption.
- Data privacy and security: Concerns about data misuse and breaches require stronger security measures.
- Standardization and interoperability: It is important to ensure that different DPI components work together seamlessly.
- Capacity building: It is necessary to enhance the skills of government officials and citizens to effectively leverage DPI.
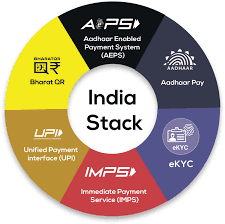
About India Stack:
- It is a set of API (Application Programming Interface).
- It creates a strong digital infrastructure to provide a variety of digital services in different sectors.
- It provides governments, businesses, startups and developers with the necessary digital infrastructure to enable remote, automated, paperless and cashless service delivery.
Way forward:
- Focus on inclusion: There is a need to bridge the digital divide through initiatives like the PM Rural Digital Literacy Mission.
- Privacy and Security: Strengthening data security framework and ensuring responsible data governance.
- As underlined in the Puttaswamy judgment, 2027, enactment and implementation of the Data Protection Act is required on priority basis.
- Strengthening existing DPIs: increasing adoption and promoting innovation in their use.
- Developing new DPI: Exploring sectors like public health, education and agriculture.
Conclusion:
- DPI has immense potential to transform India's digital landscape and empower citizens. Continuous evaluation and adaptation is necessary to ensure that DPIs remain relevant and effective.
- Tackling the current challenges and focusing on inclusive growth is the key to unlocking their full potential.
Source: The Hindu
----------------------------------------------
Main Exam Question:
What is digital public infrastructure? Suggest a way forward to address the challenges related to digital public infrastructure.