National Framework for Climate Services (NFCS)
National Framework for Climate Services (NFCS)
- Preliminary Exam: Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), National Framework for Climate Services (NFCS)
- Main Exam: Need and Importance of NFCS
October 09, 2023
Why in news:
- Recently the Government of India has decided to launch an unprecedented initiative 'National Framework for Climate Services (NFCS)' under the leadership of the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD).
- This comprehensive program aims to provide climate services and information to various sectors including agriculture, energy, disaster management, health and water resources.
NFCS
Introduction:
- NFCS draws inspiration from the Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS), a global partnership established during the Third World Climate Summit in 2009.
- India's NFCS will be in line with the global framework while tailoring its approach to the country's specific climate and stakeholder needs.
- Unlike the GFCS, the IMD will serve as the nodal agency responsible for designing and implementing the national framework.
- NFCS will address functional gaps between various agencies requiring climate services, including agencies related to hydrology, power, renewable energy, transport, dams, irrigation and healthcare at the central, state and local levels.
Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS)
- The Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS) is a partnership of governments and organizations at the global level to produce and better utilize climate information and services. The aim of the GFCS is to facilitate researchers and users of climate information and services to join hands to make informed and actionable decisions for long-term betterment.
- The objective of the GFCS is to generate high quality data from national and international databases on temperature, precipitation, wind, soil moisture and ocean state and other important weather parameters. Its objective is to create long-term historical averages of these parameters, as well as maps, risk and vulnerability analyses, assessments and long-term projections and scenarios.
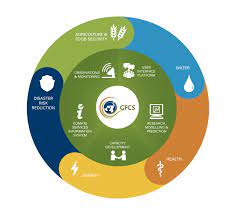
- The five major components under the GFCS are observations and monitoring, research, modeling and prediction, climate services information systems, user interface platforms and capacity building. Currently, the priority areas that the GFCS focuses on are agriculture and food security, energy, health, water and disaster risk reduction.
Functions of NFCS:
- In line with the global framework, the national framework will be based on country-specific climate and stakeholder needs. Unlike the GFCS, the nodal agency for formulation and implementation of the national framework in India will be the IMD.
- Along with the identified areas of focus, India may also add other relevant sectors such as transport, tourism and other emerging sectors from time to time.
- Initially, NFCS will work to bridge functional gaps between different agencies that require climate services. These include hydrology, power, renewable energy, transport, dams and irrigation, health agencies at central, state and other levels.
Implementation of NFCS in India:
- In 2009, Switzerland, China, Germany and the United Kingdom launched NFCS to improve climate services.
- Countries where NFCS implementation is in an advanced stage include Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Côte d'Ivoire, Gambia, Guinea, Madagascar, Moldova, Niger, Senegal, Chad, Togo, Tanzania, Vanuatu and South Africa.
- With the first workshop of NFCS held in Pune recently, India joins Cuba, Ghana, Liberia, Malawi, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Democratic Republic of Congo, Congo Brazzaville and Ethiopia.
- India will soon release the NFCS statement following consensus from key partner stakeholders.
- Although the idea of having NFCS in India dates back to 2008, it did not take off as desired. With the ever-increasing climate related uncertainties and extreme events affecting India and the world, early implementation and acceleration of NFCS will be possible when planned in mission-mode and driven by the highest decision-making office of the country.
About IMD:
- IMD was established in the year 1875.
- It is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India.
- IMD is celebrating its 150th anniversary in December 2023.
- IMD provides daily weather forecast and weather predictions for winter, summer and monsoon seasons.