
Emissions Gap Report 2023
Emissions Gap Report 2023
Important for Prelims:
Emissions Gap Report 2023, United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), Global Warming, Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHG), Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC), Net-Zero Pledges
Important for Mains:
GS-3: Highlights of Emissions Gap Report 2023, Key Initiatives for Emission Control in India
November 23, 2023
Why in news:
Recently the 14th edition of the Emissions Gap Report was released by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP).
Emissions Gap Report 2023
Title:
- The report is titled “Emissions Gap Report 2023: Broken Record – Temperatures Hit New High Yet World Fails to Cut Emissions (Again)”.
Objective:
- The purpose of releasing this report: to take urgent climate action to avoid dangerous temperature rise.
- This report provides awareness to climate scientists and organizations around the world about possible solutions to the future challenge related to greenhouse gas emissions and global warming.
key points:
- According to this report, despite the Paris Agreement, developed and developing countries around the world are moving the world towards increasing the temperature by 2.5-2.9 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels by the end of this century.
- Paris Agreement:
- This agreement was adopted in the year 2015 during the COP 21 conference to address climate change and its negative impacts.
- It is a landmark environmental agreement that requires emissions to be cut by 28-42% by 2030 to limit temperature rise to 1.5-2 degrees Celsius.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
- A new record of greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) of 57.4 gigatons of carbon dioxide equivalent (GtCO2e) was reached in the year 2022, which is 1.2% more than the previous year.
- Fossil CO2 emissions with a 100-year global warming potential are about two-thirds of current GHG emissions.
- According to the data, fossil CO2 emissions increased between 0.8-1.5% in the year 2022 which was the main contributor to the overall increase of GHG emissions.
- Emissions of fluorinated gases increased by 5.5% in the year 2022, followed by methane by 1.8% and nitrous oxide (N2O) by 0.9%.
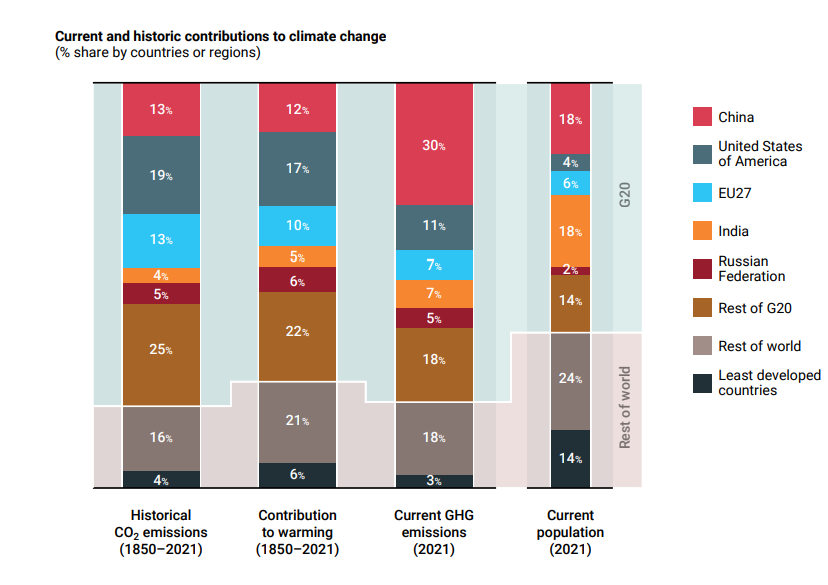
- Currently, G20 countries collectively account for 76% of global emissions.
- In the year 2022, GHG emissions of G20 countries increase by 1.2%.
- Carbon emissions have increased by China, India, Indonesia and the United States, while emissions have relatively decreased in Brazil, the European Union and the Russian Federation.
GHG emission sectors:
- Five major economic sectors contribute to emissions including: energy supply, industry, agriculture and land use, land-use change and forestry (LULUCF), transportation and buildings.
Economic sector Percentage of emissions by in the year 2022
Energy supply: 36% of total (largest source of emissions)
Industry: 25%
Agriculture and LULUCF: 18%
Transportation: 14%
Building: 6.7%
Concerns:
- Global warming is expected to reach 3 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels by the end of the century.
- Despite developed and developing countries implementing net-zero emission limits, not meeting their emissions reduction targets is a major concern.
- The probability of limiting temperature rise to 1.5°C under the current emissions scenario is only 14%.
About the Emissions Gap Report:
- The Emissions Gap Report is a spotlight report launched each year ahead of UNEP's annual climate summit.
- This report annually tracks the gap between global emissions and the level required to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Major initiatives for emission control in India:
- National Solar Mission
- PM Kisan Energy Security and Upliftment Campaign (PM-KUSUM)
- National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy
- National Offshore Wind Energy Policy
- National Hydropower Policy
- National Hydrogen Energy Mission
- National Green Hydrogen Mission
- Bharat Stage-IV (BS-IV) to Bharat Stage-VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms
- Ujala scheme
- International Solar Alliance
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Ethanol blending in India by 2025
- India updates its NDC
|
United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) About this:
|
Way forward:
- The emissions gap narrowed by policy efforts and specific action plans since the Paris Agreement is not sufficient to deal with the current situation.
- Nine countries around the world have updated their NDC programs, potentially reducing emissions by about 9% annually by 2030.
- However, further reductions are necessary to minimize the costs to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- Implementing an unconditional Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) could limit emissions growth to 2.9°C and a conditional NDC to limit it to 2.5°C.
- High emitting countries should provide financial and technical assistance to developing countries for ecological relief so that their sustainable development is not affected.
- In future, there will be a need to develop new technology to remove carbon dioxide.
- Looking to the future, all countries need to break out of the framework of inadequate action and set new records on emissions, green and equitable transition and climate finance.
Source: Indian Express
Mains Exam Question
In the light of Emission Gap Report, mention the major initiatives of India to control the emission levels.